
The solenoid's magnetic field formula provides a quantitative relationship between magnetic flux density, the magnetic constant, the number of turns, and the current. Magnetic field in a solenoid formula indicates that the magnetic field strength is directly proportional to the number of turns and the current.They can be easily controlled by adjusting the current flowing through the solenoid.Electromagnets are formed by wrapping a coil of wire (solenoid) around a ferromagnetic core.Solenoids can create controlled magnetic fields and therefore can be used as electromagnets.Its strength doesn’t depend on the distance from the axis or on the cross-sectional area of the solenoid.Magnetic field in a long solenoid is homogeneous.The core of a solenoid produces a magnetic field when an electric current passes through it.

A solenoid is a long thin loop of wire that is mostly wrapped around a metallic core.
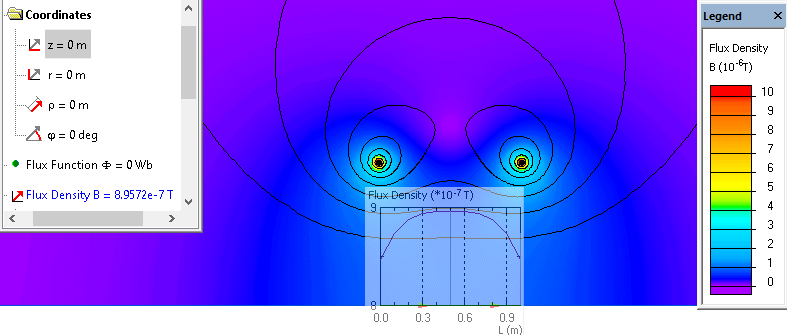
In the formula, B represents the magnetic flux density, μ 0 is the magnetic constant whose value is 4π x 10 -7 Hm -1 or 12.57 x 10 -7 Hm -1, N represents the number of turns, and I is the current flowing through the solenoid. Magnetic field in a solenoid formula is calculated as B = μ 0 nl.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
